repomgr
Repository Manager- Simple Tool for managing versions from build-pipeline
Project maintained by Ragin-LundF Hosted on GitHub Pages — Theme by mattgraham
Repository Manager
This tool is build to manage versions from CI/CD processes.
It can be used at the build-pipeline to store artifact versions and additional information to a central database. There are possibilities to differ between branch versions and projects.
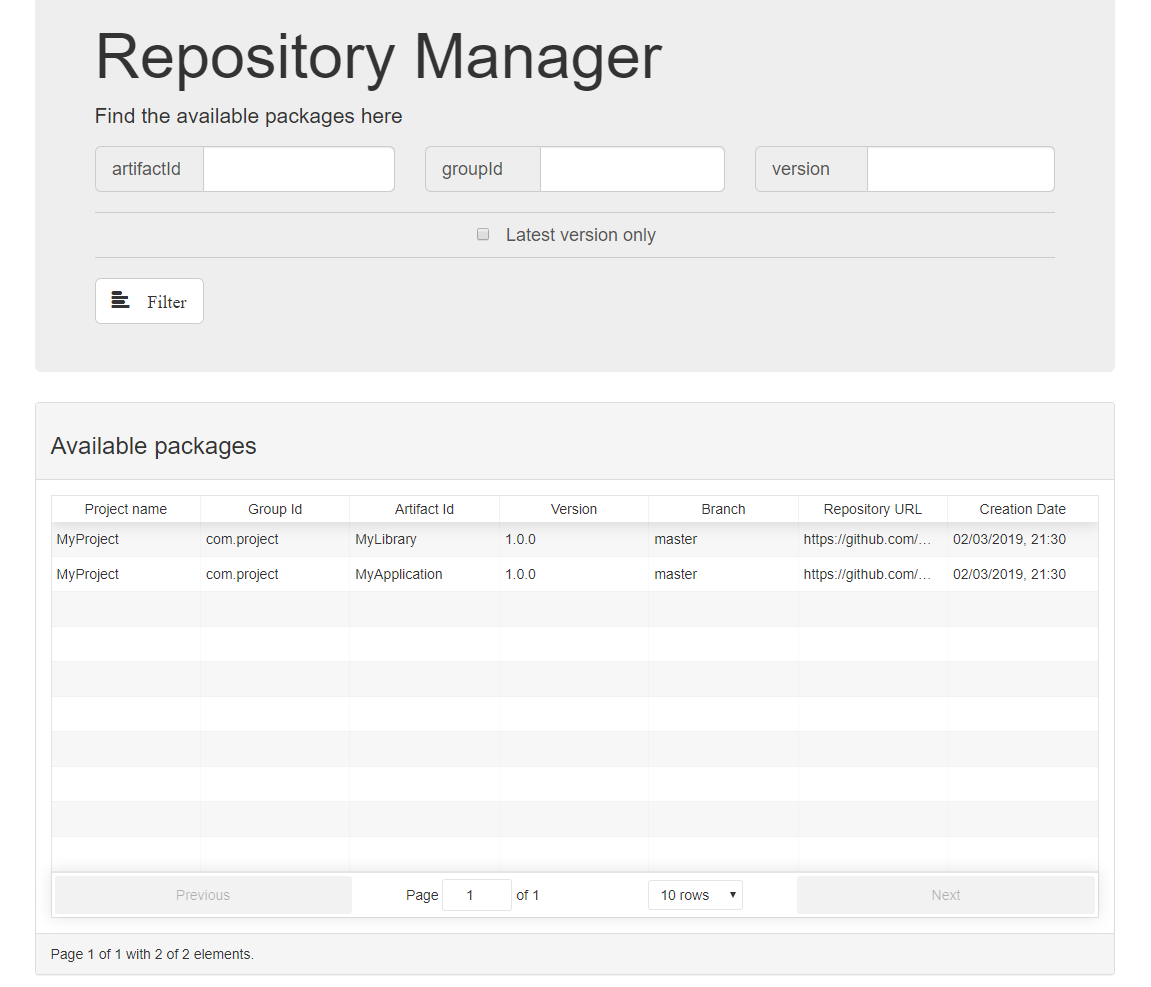
RepoMgr UI
A simple UI is included to see the available packages. http://localhost:9090/public/index.html
At the moment this UI is pre-build as static bundle and index.html!
If something is changed at the React code, the bundle.js must be rebuild.
cd src/main/resources/ui
npm install
npx webpack
Admin User
For a simple start an user will be imported at the first startup.
| Username | Password | UserId |
|---|---|---|
| admin | password | 5c6a1223-076b-4bc0-b0b7-20b0da0e23fd |
API
A swagger file is available under src/main/resources/static/swagger.yaml.
There is also a Postman collection available for some small tool support. You can find it under etc/postman/.
Security
Each endpoint is secured with a JWT token, with the exception of the /authentication/generate-token endpoint.
This endpoint needs credentials and creates a new token for the user.
Example of a JWT-token content:
{
"sub": "admin",
"scopes": [
{
"authority": "ROLE_ADMIN"
}
],
"iss": "RepoManager",
"iat": 1549061618,
"exp": 1549065229
}
User API
The Repository Manager has a simple API for managing users (create, update password, delete) and a simple role-system (ADMIN, USER) to separate users and/or tokens for every project.
Authentication API
This API offers to generate a token with credentials. With this token a pipeline can use the repository API.
Repository API
The repository API is for storing artifact information to the system.
Using from console
Create an user token
First generate a valid user token:
curl -d '{"username":"admin","password":"password"}' -H "Content-Type: application/json" -X POST http://localhost:9090/v1/authentication/generate-token
This returns something like this:
{"token":"eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJzdWIiOiJhZG1pbiIsInNjb3BlcyI6W1t7ImF1dGhvcml0eSI6IlJPTEVfQURNSU4ifV1dLCJpc3MiOiJSZXBvTWFuYWdlciIsImlhdCI6MTU0OTIyMzgxMiwiZXhwIjoxNTQ5MjI3NDEyfQ.LPki3LvCaWdkkW-O7grZ66eCKT9QdK76jsSjyLZQ4uw","userId":"5c6a1223-076b-4bc0-b0b7-20b0da0e23fd"}
The token is the new Bearer token and should be set to all privileged endpoints at the Authorization header with the Prefix Bearer :
-H "Authorization: Bearer eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJzdWIiOiJhZG1pbiIsInNjb3BlcyI6W1t7ImF1dGhvcml0eSI6IlJPTEVfQURNSU4ifV1dLCJpc3MiOiJSZXBvTWFuYWdlciIsImlhdCI6MTU0OTIyMzM5NywiZXhwIjoxNTQ5MjI2OTk3fQ.8CoevJ61fF8lDNH7EmIcsHhnbxFwE7mmOe0fXBHJtwA"
Change password of admin
It is a good idea to change the admin password now:
curl -d '{ "password": "newpassword"}' -H "Content-Type: application/json" -H "accept: application/json" -H "Authorization: Bearer eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJzdWIiOiJhZG1pbiIsInNjb3BlcyI6W1t7ImF1dGhvcml0eSI6IlJPTEVfQURNSU4ifV1dLCJpc3MiOiJSZXBvTWFuYWdlciIsImlhdCI6MTU0OTIyMzM5NywiZXhwIjoxNTQ5MjI2OTk3fQ.8CoevJ61fF8lDNH7EmIcsHhnbxFwE7mmOe0fXBHJtwA" -X PUT "http://localhost:9090/v1/users/5c6a1223-076b-4bc0-b0b7-20b0da0e23fd/password"
If this was successful, a response like the following should be there:
{"userId":"5c6a1223-076b-4bc0-b0b7-20b0da0e23fd","valid":true}
Creating new users for projects
Now it is time to create new users. Each project can have its own user with its own token.
curl -d '{"password":"myprj","username":"user001","projectName":"MyProject","role":"ROLE_USER"}' -H "accept: application/json" -H "Authorization: Bearer eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJzdWIiOiJhZG1pbiIsInNjb3BlcyI6W1t7ImF1dGhvcml0eSI6IlJPTEVfQURNSU4ifV1dLCJpc3MiOiJSZXBvTWFuYWdlciIsImlhdCI6MTU0OTIyMzM5NywiZXhwIjoxNTQ5MjI2OTk3fQ.8CoevJ61fF8lDNH7EmIcsHhnbxFwE7mmOe0fXBHJtwA" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -X POST "http://localhost:9090/v1/users"
This results (hopefully) in such a response:
{"userId":"89955603-defe-4aea-b2ee-dcc89820e22e","valid":true}
Before this user can be used in a pipeline, the user has to generate a token via the authentication-API like at the first step, but with the user credentials.
If valid is false, then something went wrong (mostly username already exists).
Insert a new version from build-pipeline
Now a jenkins can post a new build version information with the following command:
curl -d '{"projectName": "MyProject", "branch": "master", "artifact": {"groupId": "com.project", "artifactId": "MyLibrary", "version": "1.0.0"}, "repositoryUrl": "https://github.com/Ragin-LundF/repomgr", "creationDate": "2019-03-02T20:30:35.420+0000", "type": "LIBRARY", "latestVersion": true, "description": "# RepoManager # Dependencies and version management tool. You can also use Markdown here."}' -X POST "http://localhost:9090/v1/repositories" -H "accept: application/json" -H "Authorization: Bearer eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJzdWIiOiJhZG1pbiIsInNjb3BlcyI6W1t7ImF1dGhvcml0eSI6IlJPTEVfQURNSU4ifV1dLCJpc3MiOiJSZXBvTWFuYWdlciIsImlhdCI6MTU0OTIyMzgxMiwiZXhwIjoxNTQ5MjI3NDEyfQ.LPki3LvCaWdkkW-O7grZ66eCKT9QdK76jsSjyLZQ4uw" -H "Content-Type: application/json"
The result of this POST should look like:
{"_status":true}
Querying the repository
Last but not least, there is a possibility to ask for versions with the search:
curl -d '{"groupId":"com.project","artifactId":"MyLibrary","latestVersion":true}' -X POST "http://localhost:9090/v1/repositories/search" -H "accept: application/json" -H "Content-Type: application/json"
Which should result in:
{"versionInformation":[{"projectName":"MyProject","branch":"master","groupId":"com.project","artifactId":"MyLibrary","version":"1.0.0","repositoryUrl":"https://github.com/Ragin-LundF/repomgr","creationDate":"2019-03-02T20:30:35.420+0000"}],"page":{"totalElements":1,"totalPages":1,"currentPage":1,"numberOfElements":1}}
With the "latestVersion":true flag at the request, Repository Manager searches only for the latest version.
For more informations about the filtering possibilities, please look into the swagger.yaml file.
Deployment
Configuration option
The JAR file is a self-runnable JAR and can be started with:
java -jar repomanager-x.x.x.jar
To support simple configuration, there are some additional programm arguments:
| Argument | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
| –repoadmin_db_host | Host or IP of the database | localhost |
| –repoadmin_db_port | Port of the database | 5432 |
| –repoadmin_db_username | The database username | repomgr |
| –repoadmin_db_password | The database user password | repomgr |
| –repoadmin_db_database | The database | repomgr |
| –repoadmin_db_jdbc | JDBC server name (jdbc://REPO_MAN_DB_JDBC:/…) | postgres |
| –repoadmin_db_driver | JDBC driver class | org.postgresql.Driver |
At the moment only a postgres driver is included.
To support other databases, it is possible to store the driver to a subdirectory and to start the application like this:
java \
-cp repomanager-x.x.x.jar \
-Dloader.path=<path_to_your_additional_jars> \
org.springframework.boot.loader.PropertiesLauncher
Docker support
Docker image
The existing Dockerfile builds the application with an alpine linux and OpenJDK 11.
Environment variables
The image needs the following environment variables for application configuration.
| Variable | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
| REPO_MAN_DB_HOST | Host or IP of the database | localhost |
| REPO_MAN_DB_PORT | Port of the database | 5432 |
| REPO_MAN_DB_USER | The database username | repomgr |
| REPO_MAN_DB_PASS | The database user password | repomgr |
| REPO_MAN_DB_DATABASE | The database | repomgr |
| REPO_MAN_DB_JDBC | JDBC server name (jdbc://REPO_MAN_DB_JDBC:/…) | postgres |
| REPO_MAN_DB_DRIVER | JDBC driver class | org.postgresql.Driver |
Building an image
docker build -t repo-mgr .
Running the image
After the build, the image can be started like:
docker run -d -p 9090:9090 --env REPO_MAN_DB_JDBC=postgres --env REPO_MAN_DB_DRIVER=org.postgresql.Driver --env REPO_MAN_DB_HOST=localhost --env REPO_MAN_DB_PORT=5432 --env REPO_MAN_DB_USER=repomgr --env REPO_MAN_DB_PASS=repomgr --env REPO_MAN_DB_DATABASE=repomgr --name=RepoManager repo-mgr
Stop the image with:
docker stop RepoManager
Using docker-compose
The pre-configured docker-compose.yaml builds the server image and a postgres database.
Starting the complete environment:
docker-compose up -d
Stopping the environment:
docker-compose down
Screenshot